3D-Printed Electronics: Innovation In Smart Wearables
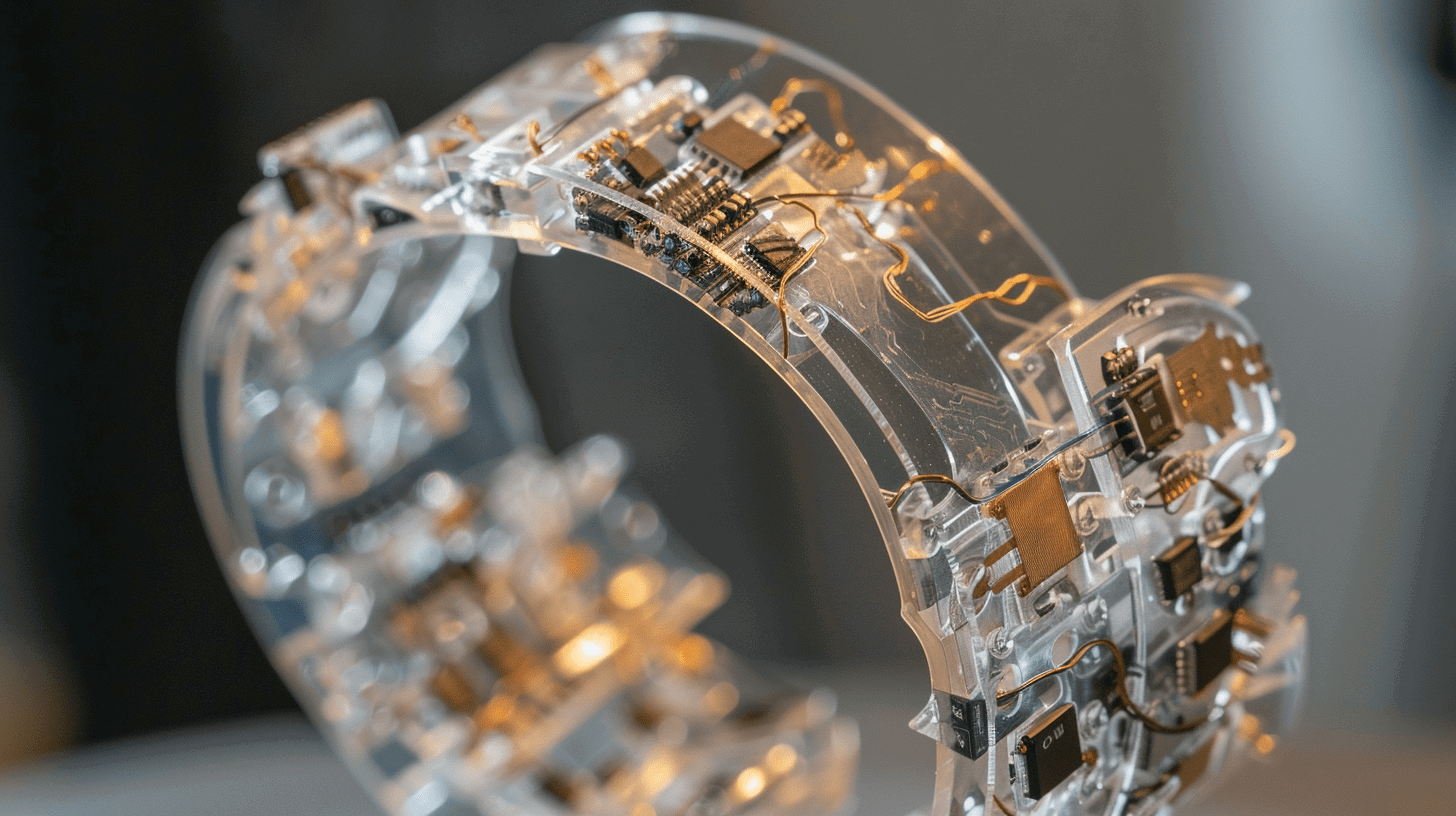
The combination of additive manufacturing and electronics has significantly advanced the progress of 3D-printed electronic wearables, placing them at the forefront of technological advancement. This article explores how 3D printing technology is transforming the design and capabilities of smart wearables.
Materials and Fabrication Techniques
The foundation of 3D-printed electronic wearables is based on the use of advanced materials and complex manufacturing methods. Conductive filaments play a crucial role in embedding circuitry directly into printed items, facilitating the seamless integration of electronic features like sensors, circuits, and connectors. Techniques such as fused deposition modeling and stereolithography are commonly utilized to achieve precise results and material flexibility, allowing for the development of intricate, multifaceted devices.
Customization
3D printing provides unique customization opportunities for electronic wearables. By using accurate 3D body scans, these devices can be tailored to fit the user's individual measurements, improving comfort and maximizing their technological performance. This level of precision is especially important for devices that need to interface closely with the skin, such as health monitoring bands and neurological stimulators, guaranteeing precise placement of sensors and electrodes.
Integration of Electronics and Functionality
3D printing is advantageous for sustainability as it minimizes waste by using additive processes, which differs from the subtractive processes used in traditional electronics manufacturing. Additionally, 3D printing allows for on-demand production, reducing overproduction and excess inventory. There are also possibilities for advancements in organic electronics and biodegradable materials in the future, further contributing to a decreased environmental impact of electronic wearables.
Challenges and Innovations
Despite the progress, challenges remain in improving the durability and reliability of printed electronics, as well as improving the integration of soft and hard materials. Ongoing research is addressing these issues through the development of new materials and printing processes that increase the durability and functionality of electronic wearables.

Introduction to Additively Manufactured Electronics and What It Can Do for You
The research paper was prepared by the J.A.M.E.S. engineering team and primarily focuses on the advantages of Additively Manufactured Electronics (AME) over traditional printed circuit board (PCB) technology.
Related Articles

Horizon Announces Expansion Of Service To Include Subcontract Micro-AM Production And Design Support







