3D Printing Materials Guide
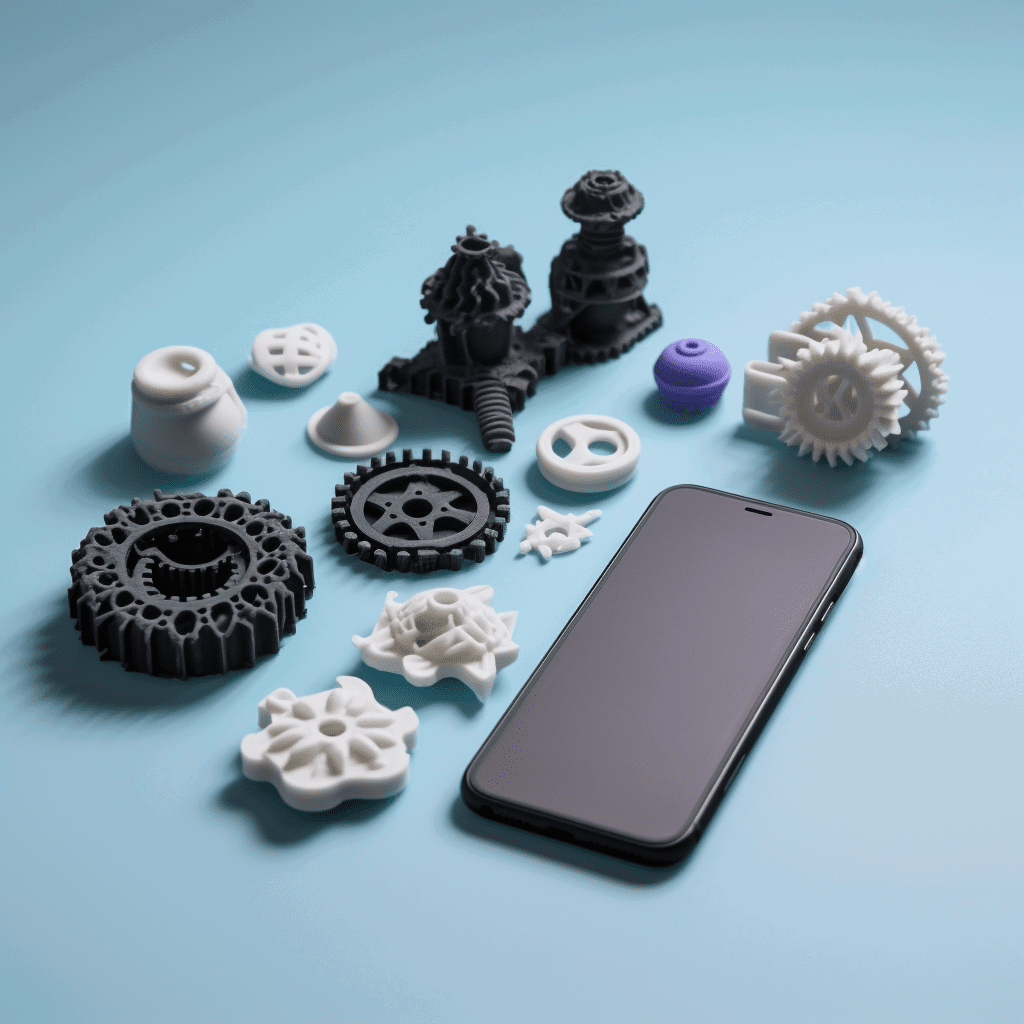

The technology of 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is an advancement that permits the production of three-dimensional objects through digital data. An essential determinant in this process involves selecting an appropriate material type for such printing endeavors since different materials are available and possess distinct attributes. This article will explore various customary materials utilized for 3D printing purposes.
Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a type of thermoplastic that has become quite popular as the world searches for more and better bio-based polymers to cope with the dwindling supply and steady increase in price of traditional petrochemical derived plastics suited especially for use in 3D printing. PLA, derived from renewable sources (corn-starch or sugarcane), is reported as low toxic and environmentally friendly. It has easily printable/check feature with high-quality results in glossy form. The majority of 3D printing is the fabrication of low-stress objects like figurines, toys and other decorative items. As a result, PLA is one of most used filaments in additive manufacturing this days.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is a thermoplastic utilized in 3D printing. Its strength and heat resistance makes it a viable choice for producing parts like gears, electronic housings and even automotive components. ABS is harder to print as well, including more warping issues and a much higher percentage of shrinkage rate when compared with polylactic acid (PLA). ABS also produces harm gas during printing.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene Terephthalate, that is PET in short and a shape of thermoplastic polymer resin which mostly used for making drink bottles. Its strength and durability, combined with its printability make it a great choice for creating functional parts like gears bearings and mechanical components. It is also high performing as a chemistry and water-resistant material, which allows to make things resistant in harsh conditions where moisture or chemicals are present.
Nylon
Nylon is a flexible yet high strength material that has been used in textile production, but also made its way into 3D printing. Nylon, on the other hand has high melting point and it can absorb moisture from air but results are really very good even though printing with Nylon is difficult. For both SLA and DLP 3D printers, these create incredibly strong parts with excellent flexibility and durability over repeated use which makes them the default choice for manufacturing complex mechanical objects such as gears or hinges.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Thermoplastic Polyurethane: A flexible and elastic material that is often used to make flexible goods like phone cases, shoe soles, etc. As TPU offers easy of printability and high-quality final output which is durable yet can withstand a great punch, this makes it well suited for objects that require flexibility and shock absorbency - things like watch bands, limb prosthetics or mobile device cases.
Metal
Metal as a material in 3D printing is fairly new: it has become widely used only for application in industrial areas along with plastic. The manufacturing of metal objects with 3D printing is done via Direct Metal Laser Sintering ( DMLS ), using metallic powders to obtain the desired profiles. This is especially advantageous for the manufacture of highly complex metal components which are difficult or impossible to produce using conventional manufacturing processes. Therefore it is very common in industries like aerospace and automotive industry usually associated with medical fields implement this technology within their operations.
Related Articles
Horizon Successfully Manufactures Corrugated Horn Antenna

J.A.M.E.S Partners With APES Forge Strategic Partnership To Boost AME Innovation

Additive Manufacturing Of Interposers With Curved Vias For Microelectronics Packaging

APES Partners With IDS To Advance 3D Printed Electronics









