Cube Satellites: Paving The Way For The Future Of Space Activities
Concept
This AME design has the status of concept. A first design concept is established, a complete explanation of the targeted functionality is included, and the targeted printer technology has been provided.
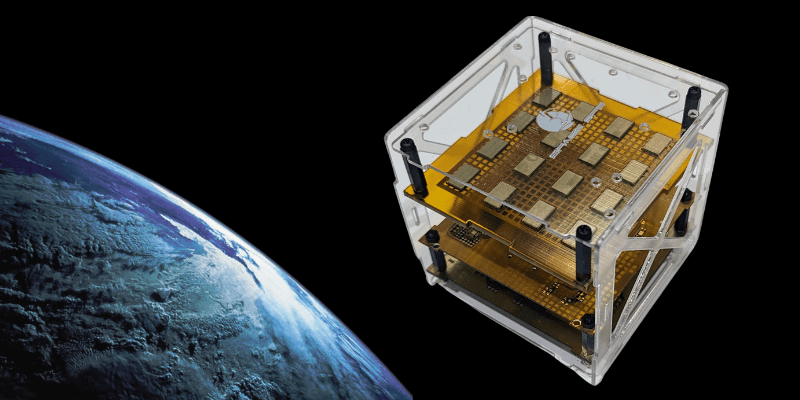
Exploring the vast expanses of space has always captivated human imagination, driving us to uncover its mysteries and push technological boundaries. In recent times, Cube Satellites have emerged as pivotal players in shaping the future of space endeavors. These miniature wonders, no larger than a Rubik's Cube, are revolutionizing space exploration, enhancing accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. In this blog post, we delve into the role Cube Satellites are poised to play in the evolving landscape of space activities.
THE EVOLUTION OF CUBE SATELLITES:
Cube Satellites, or CubeSats, have evolved significantly since their inception. Initially conceived as educational tools, these standardized satellites have transcended classroom use, finding applications in scientific research, Earth observation, technology demonstrations, and even interplanetary missions. Private organizations are extending their reach through cost-effective CubeSat projects, deviating from traditional large, expensive satellites. CubeSats' appeal lies in their compact size, affordability, and swift development cycles, making them ideal for diverse space missions.
KEY FEATURES AND BENEFITS:
Miniaturization: Cube Satellites adhere to standardized sizes and weights, measured in "units" (1U, 2U, 3U, etc.), with a 1U CubeSat measuring 10x10x10 centimeters. This standardization facilitates easy integration into launch vehicles and enables collaboration on multi-satellite missions.
Affordability: CubeSats' small size and simplicity contribute to their affordability, democratizing space access for academic institutions, startups, and individual researchers. This opens up opportunities for participation in space missions previously reserved for larger, government-sponsored projects.
Versatility: CubeSats have become versatile platforms customizable for various purposes. They can carry diverse payloads, including cameras, sensors, and scientific instruments, making them adaptable to missions ranging from Earth observation to deep space exploration.
Swift Development: The streamlined design and construction process of CubeSats allow for rapid development cycles, crucial for staying ahead in the dynamic field of space exploration, where mission objectives can quickly evolve.
TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATIONS DRIVING CUBE SATELLITE ADVANCEMENTS:
Cube Satellites have emerged as pioneers of innovation, providing a cost-effective means for scientific research and data collection. As Cube Satellites are no longer confined to traditional propulsion methods. Researchers are pushing the boundaries by exploring innovative systems such as ion drives and solar sails. These advancements are not merely about reaching new destinations but also about enhancing maneuverability and longevity, thereby expanding the operational capabilities of Cube Satellites. As we look to the future, propulsion systems are poised to redefine the way these miniature satellites navigate the cosmos.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Cube Satellite technolgy, the integration of cutting-edge components such as 3D printed sensors and advanced RF communication technologies stands out as a pivotal advancement. Researchers are channeling their efforts into refining communications capabilities, recognizing the indespensable role it plays in the success of Cube Satellite missions. Miniaturized antennas, crafted through innovative AME Technologies, such as the DragonFly IV System, are becoming instrumental in ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission. Additionally, the incorporation of high-data-rate and communication systems further enhances the real-time monitoring of satellite activities, enabling a seamless flow of information between Cube Satellites and Earth. This convergence of 3D printed sensors and RF communication technologies, not only bolsters the reliability of Cube Satellite networks but also exemplifies the constant pursuit of innovation within the realm of space exploration.
HOW NANO DIMENSION'S AME TECHNOLOGY IS CHANGING PRODUCTION:
Cube Satellites stand at the forefront of innovation, promising to reshape the space activities landscape with their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and rapid development cycles. As technology advances and a growing community of CubeSat enthusiasts emerges, the future holds the promise of these miniature satellites pushing the boundaries of achievements in space exploration. Cube Satellites are not merely tools; they are pioneers opening new frontiers in cosmic exploration, thus making space more accessible and helping to inspire a new generation of space enthusiasts.
Within the domain of Cube Satellite development, the utilization of 3D printing for electronics stands out as a potent remedy for the obstacles encountered by researchers and engineers. Providing customization, expeditious prototyping, cost-effectiveness, and hastened development, 3D printing enables CubeSat developers to adeptly manage the intricacies of in-house production. As technological progress persists, the smooth assimilation of 3D printing into Cube Satellite development procedures holds the potential to unveil fresh opportunities, fostering greater accessibility in space exploration and sparking a new phase of innovation in the cosmos.
TO LEARN MORE ABOUT AME AND ITS MPACT ON SPACE ACTIVITIES, DOWNLOAD THE NEW PAPER HERE.
Related Articles

High Frequency Solution-processed Organic Field-effect Transistors With High-resolution Printed Short Channels

FED Working Group For 3D Electronics - New English White Paper Edition 2024

FED White Paper Edition 2024: Part 4 AME Classification (Class 5 (4D))




