Advances In Miniaturization: How GED Is Making Electronics Smaller And More Powerful
Advancements in Miniaturization: How GED Makes Electronics Smaller and More Powerful
Modern electronic products are required to meet the highest standards: smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient—all without compromising quality. Especially in the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries, miniaturization is the key to driving innovation. For over 38 years, GED has delivered expertise, creativity, and a sharp focus on compact and high-performance electronics.
The Fundamentals of Miniaturization
Miniaturization means reducing electronics to their essential core without compromising functionality. It’s about achieving maximum efficiency in the smallest possible space—a critical requirement for medical technology, communication devices, and IoT applications.
According to the German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers' Association (ZVEI), the global microelectronics market is projected to grow to $602 billion by 2025. This demonstrates the enormous demand for powerful and space-saving electronics. GED combines practical application with research: In numerous projects, such as those focusing on IoT sensor technology, GED has built a wealth of knowledge that directly informs customer projects. The goal: solutions that are not only compact but also economically and technically superior.
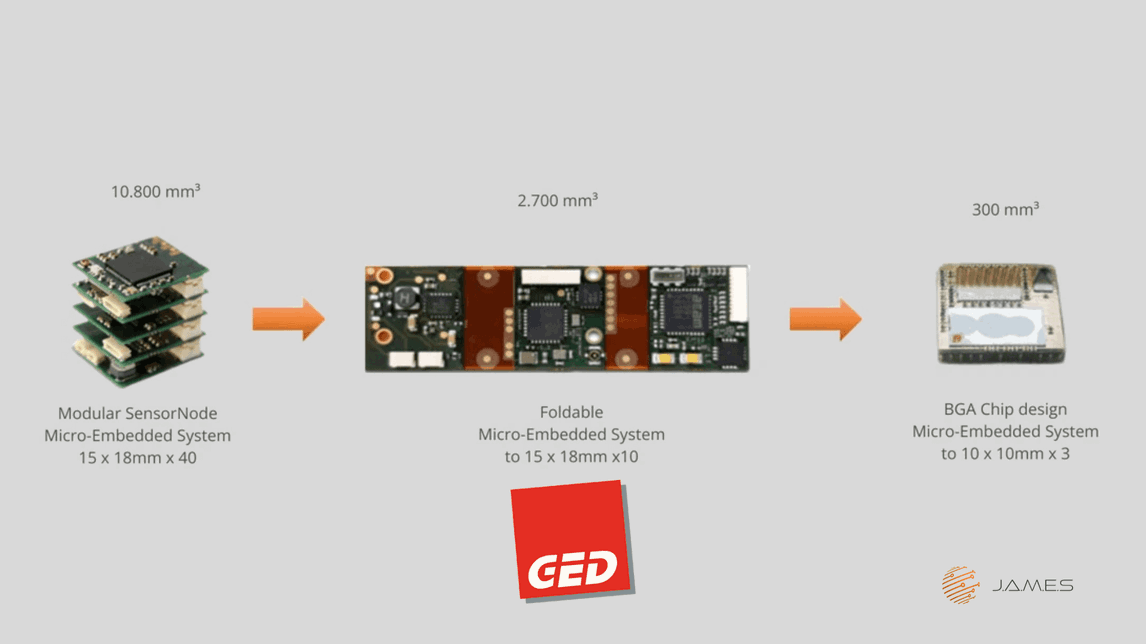
3D Miniaturization: More Than Just Downsizing
Flat designs quickly hit their limits—this is where GED’s 3D miniaturization comes into play. By integrating components three-dimensionally, spatial efficiency is significantly improved. The result: complex systems with minimal space requirements.
Key Technologies:
-
HDI-Embedded: Bare dies are directly integrated into the PCB to save space and weight.
-
Microvias: GED has utilized this technology since 1992 to achieve ultra-compact formats for fine-pitch and high-pin-count components.
-
High-current PCBs: In 2007, GED developed a PCB capable of carrying 300 amps through copper connections—a milestone for e-mobility and energy technology.
GED leverages this momentum to create increasingly intelligent and efficient solutions.
Practical Applications: GED Solutions in Action
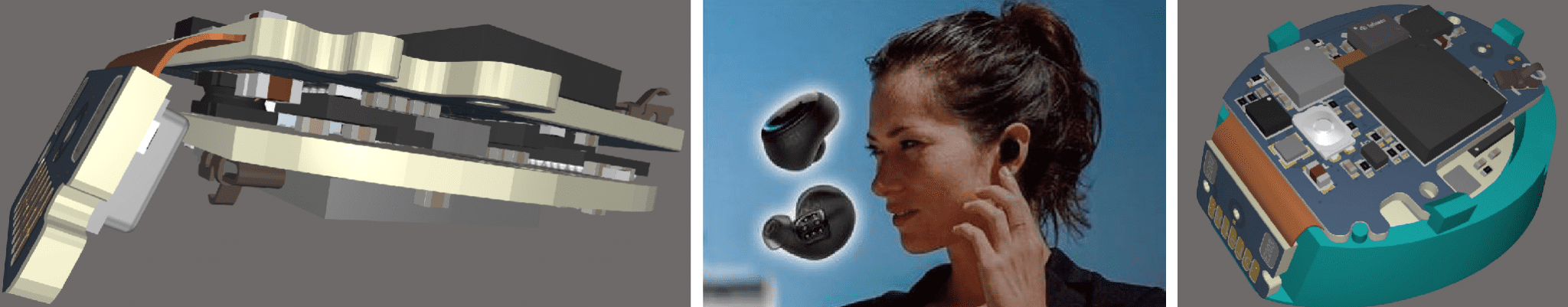
Hearables: Miniaturization in Millimeter Scale
In a hearables project, GED developed a 10-layer HDI Starflex PCB, which fits into a fingernail-sized housing.
Challenges and Solutions:
-
Collaborating with the customer to optimize the circuit design.
-
Coordinating with manufacturing partners to mass-produce 100,000 units annually.
-
Results: The first production run of PCB´s was a success within just 12 weeks.
Medical Technology: High-Level Sensor Integration
GED developed a Helath sensor demonstrator within three months. Five different sensors were integrated into a single compact module.
Results: The design enables more precise patient monitoring while reducing device size. Rapid development led to both a minimum viable product and a scalable production model.
GED and the Use of J.A.M.E.S
The J.A.M.E.S platform provides GED with a robust foundation for exchanging insights into trends and technologies also in additive manufacturing electronics. New approaches are tested here, expanding the potential of 3D printing in PCB manufacturing.
For instance, freeform electronics and stacked layers allow for even more efficient PCB solutions. GED capitalizes on these opportunities to remain at the forefront of innovation.
Future Prospects
GED continues to advance miniaturization by developing new approaches to 3D integration. With innovative materials and advanced manufacturing methods, GED lays the groundwork for even more powerful electronics.
With over 38 years of experience in design and interconnection technology (AVT), miniaturization, and serial production, GED is a leading player in the industry. Hanno Platz, owner of GED, initiated and shaped the Working Group for 3D Electronics.
As a trusted partner for excellence in electronics development, GED stands for progress, pragmatism, and a vision to make technology smarter and more accessible.
Related Articles

Voltera: Printing ECG Electrodes With Biocompatible Gold Ink On TPU